
- #DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK DRIVERS#
- #DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK DRIVER#
- #DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK FULL#
- #DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK SOFTWARE#
You can also use a host network for a swarm service, by passing -network host to the docker service create command.
#DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK DRIVER#
Let's create a container and see how the bridge network works. The host networking driver only works on Linux hosts, and is not supported on Docker Desktop for Mac, Docker Desktop for Windows, or Docker EE for Windows Server. The Docker bridge driver automatically installs rules in the host machine so that containers on different bridge networks cannot communicate directly with each other.īy default, the Docker server creates and configures the host system's an ethernet bridge device, docker0.ĭocker will attach all containers to a single docker0 bridge, providing a path for packets to travel between them.
#DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK SOFTWARE#
In docker, a bridge network uses a software bridge which allows containers connected to the same bridge network to communicate, while providing isolation from containers which are not connected to that bridge network. When we start Docker, a default bridge network is created automatically, and newly-started containers connect to it. Note that this network has no containers attache to it yet. If we want to get more info about a specific network, for example, the bridge: The bridge is the one we're interested in this post. Now, let's see the default networks on our local machine:Īs we can see from the output, Docker provides 3 networks. That's it for today.To see the default docker network, we may want to remove unused networks that we built while we were playing with docker. ❯ docker network inspect -f ' else empty end'Ĭhange bridge to some other network, and you'll get all the containers and their IP addresses like this.
#DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK DRIVERS#
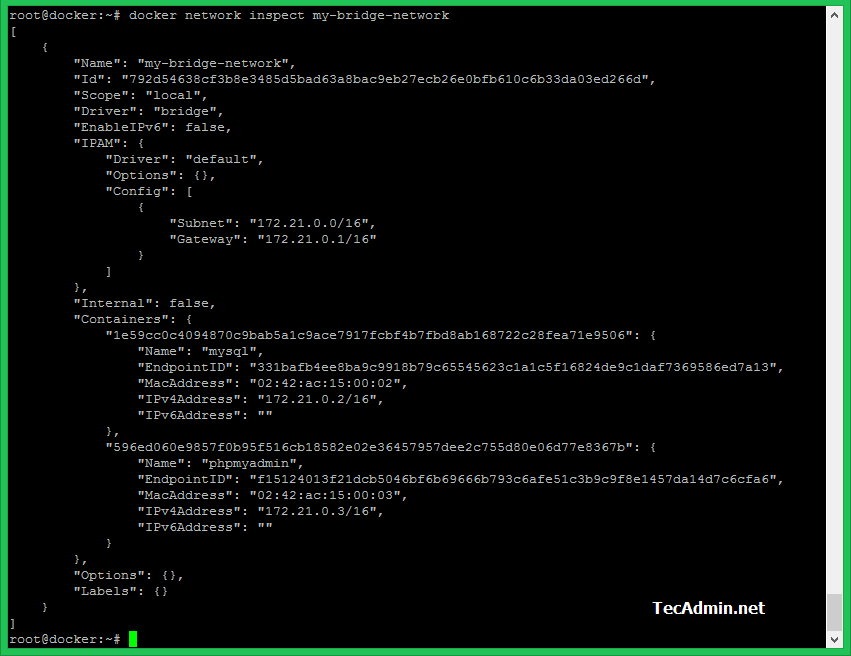
If you still need the original request, directly exposing the container, you can use macvlan or ipvlan network drivers to give the container an externally reachable IP. I'm going to filter the output since for this demonstration I don't need all the data that inspect is going to explode out. This requires that the host have each of the IP addresses configured which has been described in other SE Q&As. You can get more details about this network by running the docker network inspect bridge command.

The bridge network is the default network every container is going to be connected to if none is specified explicitly. Bridge networking leverages iptables for NAT and port-mapping, which provide single-host networking. Ignore the last two and focus on the first network. A Linux bridge provides a host internal network in which containers on the same host may communicate, but the IP addresses assigned to each container are not accessible from outside the host. You can get the list of networks using the following command docker network lsĬonsider my list below: ❯ docker network ls There are mainly two types of networks, the default or predefined networks and the user-defined networks. If two containers take on IP addresses from the same pool, they're going to be able to communicate with each other. Think of docker network as a pool of available IP addresses. This network is called a "docker network".
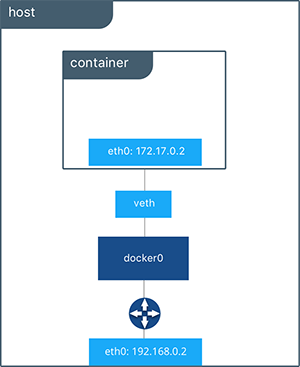
This communication is achieved by having at least two network interfaces associated with each of these two containers, both interfaces being connected to the same network. The frontend has to communicate with the database, otherwise, it just won't work. With this command, Docker will set up the standard network model: It will create a veth interface pair.
There are two services, one is the web server that serves the frontend, and another is the backend, the database. Start your docker container, using the -p option to bind exposed ports to an ip address and port on the host: docker run -d -name web -p 10.12.0.117:80:80 larsks/simpleweb. Depending on the purpose of the software, one service may need to communicate with another.įor example, consider WordPress. Each of these softwares is broken down into microservices and then packaged as containers.
#DOCKER IP HOST NETWORK FULL#
Software can have a multitude of purposes, from possibly simple text processing to a full web server, hosting your private files. How docker containers communicate?ĭocker is a tool for packaging and delivering software to the masses using containerization technology. I'll explain that to you in the next section followed by some other methods of getting the IP address of a running docker container. To understand that, you need to understand how containers communicate with each other. You may also use grep command to get just the lines matching the string "IPAddress".ĭon't be alarmed if your container has more than one IP address. Go towards the end and look into the Networks section to get the container's IP address. The inspect command gives you many details about the container you are inspecting. Don't know the container's name or ID? Use the command sudo docker ps.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
